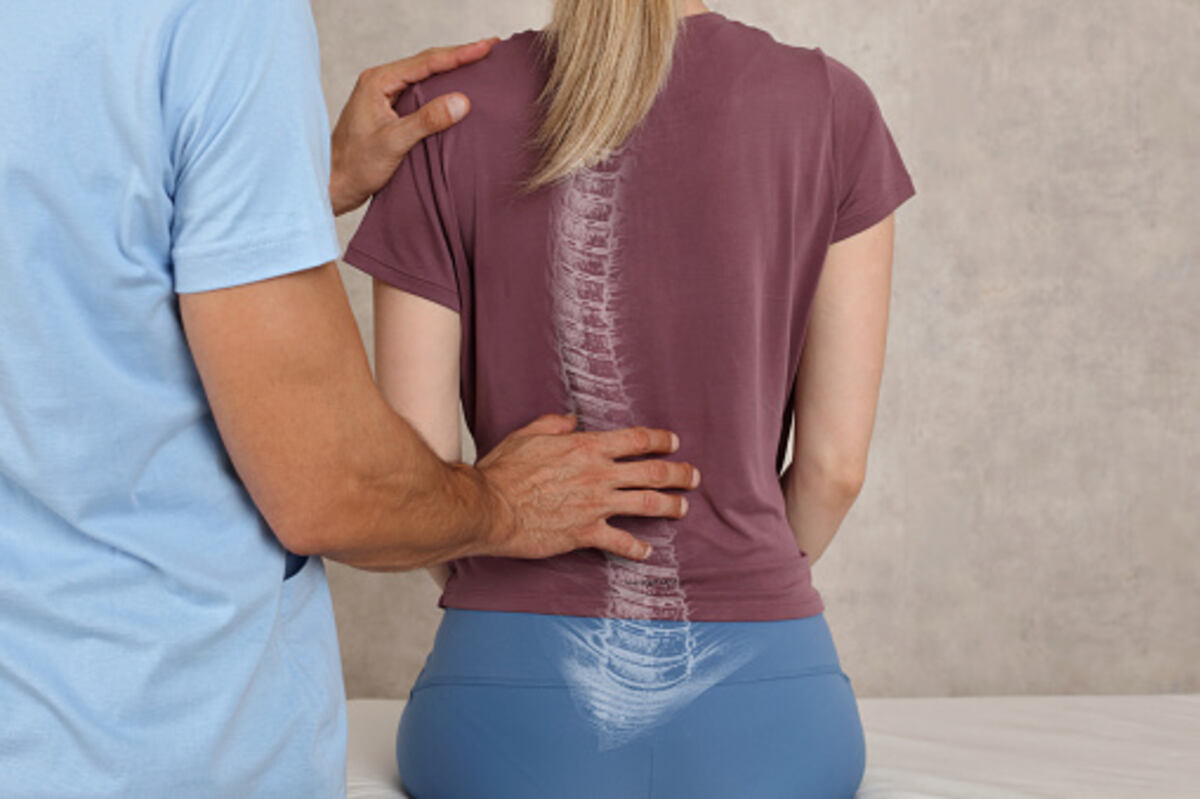
The curvature of the spine is a medical condition characterized by a rounded or twisted spinal column. It is a common condition affecting many people worldwide, ranging from children to adults. This article will discuss some of the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for this condition.
The curvature of the spine
Scoliosis is a spine deformity, and it can have severe consequences if not treated early. Early treatment may include braces or spinal fusion surgery, which helps reduce the curve and prevent it from worsening. During this procedure, the surgeon will use screws, bone grafts, or metal rods to correct the curvature of the spine. After this procedure, children can return to school and participate in sports after three to six months. However, they should avoid participating in contact sports or horse riding for at least a year and must wear a back brace for up to six months.
The most common symptoms of scoliosis are chest wall prominence and back asymmetry. Typically, adolescent girls will notice that their chests are not proportionate to their bodies. They may also experience shoulder asymmetry or a general posture imbalance in the coronal plane.
Causes
Scoliosis is a spinal deformity. In most cases, it will disappear once the underlying cause is resolved. However, in severe cases, spinal surgery may be necessary. In mild cases, bracing may be sufficient to prevent the curve’s progression. If you suspect your child has scoliosis, visit your primary care physician. They may refer you to a specialist in spine disorders, such as an orthopedic surgeon or physiatrist.
Although scoliosis is not life-threatening, severe cases can cause significant pain and affect a person’s quality of life. It can also lead to problems with lung function and the abdominal organs. Severe cases may also lead to arthritis and degeneration of intervertebral discs. It’s important to note that scoliosis is rare in children. It can be caused by several causes, including spinal cord lesions and tumours.
Treatment will depend on the specific cause of scoliosis. Most cases can be corrected with exercises and spinal bracing. A healthcare provider can also thoroughly examine a patient’s spine to detect any deformities. A healthcare provider will also check for lateral curvature, which means that the vertebrae bend. This may be obvious through the asymmetry of the shoulder or hips.
Symptoms
Scoliosis is a common ailment that affects the spine and can interfere with movement and posture. It is usually found in early childhood, although it can occur during adulthood. The underlying cause of scoliosis is unknown, but it tends to run in families. It is not caused by carrying heavy backpacks, poor posture, or sports. Instead, it’s a spine disease that’s in the genes.
The best time to seek treatment for scoliosis is during the adolescent years. The condition is more common in young children and adolescents, and early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to preventing further damage. Although early treatment is critical for children and adolescents with moderate curves, surgical treatment can be an option for more advanced cases.
Scoliosis can also affect the lungs, so seeking medical attention as early as possible is essential. If left untreated, scoliosis can lead to pulmonary heart disease. In this case, the child will likely need additional testing and care from an orthopedic specialist. Fortunately, treatments available can correct minor curves and help children return to an active lifestyle.
Treatment
Treatment of scoliosis involves using various techniques, including X-rays and MRIs. The doctor will also take a detailed medical history and look for changes in the child’s growth over the past few months. Then, he may have the child bend forward from the waist to check for abnormalities. Plain X-rays are also performed to confirm the diagnosis. The doctor may also order a spine MRI to determine the curvature’s underlying cause.
The majority of scolioses are mild and non-progressive. Nevertheless, some cases of scoliosis progress faster than others, especially in adolescents. A patient’s age, menstrual status, and radiographic parameters will determine the potential for growth in each patient. For example, boys typically grow until they reach the age of 14, while girls continue to grow until they hit puberty. In some cases, surgical correction may be necessary.
Surgical treatment of scoliosis can be done in several ways. The most common method is spinal fusion, which removes the soft tissue between vertebrae and replaces it with bone or metal. A spinal fusion surgery will fuse two bones using a rod or bone graft. This procedure may be complicated and requires limited activity for three to six months. Although it is highly effective in correcting scoliosis, the risks associated with this surgery include bleeding, infection, and even nerve damage.